| 1 | 1760 | - 25 Oct 1760—29 Jan 1820: King George III's reign

George III was the third British monarch of the House of Hanover, but unlike his two predecessors, he was born in Great Britain, spoke English as his first language, and never visited Hanover. His reign was marked by a series of military conflicts involving his kingdoms, much of the rest of Europe, and places farther afield. Early in his reign, Great Britain defeated France in the Seven Years' War, becoming the dominant European power in North America and India. However, many of Britain's American colonies were soon lost in the American War of Independence. Further wars against revolutionary and Napoleonic France from 1793 concluded in the defeat of Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo in 1815.
Later in life, George III had recurrent mental illness. After a final relapse in 1810, a regency was established, and George III's eldest son, George, Prince of Wales, ruled as Prince Regent.
|
| 2 | 1812 | - 8 Jun 1812—9 Apr 1827: Earl of Liverpool - 22nd British Prime Minister

Robert Banks Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool, (7 June 1770 – 4 December 1828) was a British statesman and Prime Minister (1812–27). As Prime Minister, Liverpool called for repressive measures at domestic level to maintain order after the Peterloo Massacre of 1819. He dealt smoothly with the Prince Regent when King George III was incapacitated. He also steered the country through the period of radicalism and unrest that followed the Napoleonic Wars. He favoured commercial and manufacturing interests as well as the landed interest. He sought a compromise of the heated issue of Catholic emancipation. The revival of the economy strengthened his political position. By the 1820s he was the leader of a reform faction of "Liberal Tories" who lowered the tariff, abolished the death penalty for many offences, and reformed the criminal law.
|
| 3 | 1818 | - 24 Dec 1818: James Joule born

James Prescott Joule (24 December 1818 – 11 October 1889) was an English physicist, mathematician and brewer, born in Salford, Lancashire. Joule studied the nature of heat, and discovered its relationship to mechanical work. This led to the law of conservation of energy, which in turn led to the development of the first law of thermodynamics. The SI derived unit of energy, the joule, is named after him.
Joule worked with Lord Kelvin to develop an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, which came to be called the Kelvin scale. Joule also made observations of magnetostriction, and he found the relationship between the current through a resistor and the heat dissipated, which is also called Joule's first law. His experiments about energy transformations were first published in 1843.
|
| 4 | 1820 | - 29 Jan 1820—26 Jun 1830: King George IV's reign

George IV was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover following the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten years later. From 1811 until his accession, he served as Prince Regent during his father's final mental illness.
George IV led an extravagant lifestyle that contributed to the fashions of the Regency era. He was a patron of new forms of leisure, style and taste. He commissioned John Nash to build the Royal Pavilion in Brighton and remodel Buckingham Palace, and Sir Jeffry Wyattville to rebuild Windsor Castle.
His charm and culture earned him the title "the first gentleman of England", but his dissolute way of life and poor relationships with his parents and his wife earned him the contempt of the people and dimmed the prestige of the monarchy.
- 12 May 1820: Florence Nightingale born
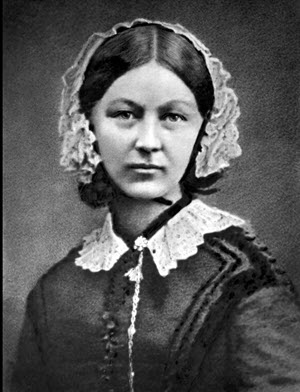
Florence Nightingale, (12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English social reformer and statistician, and the founder of modern nursing.
Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War, in which she organised care for wounded soldiers. She gave nursing a favourable reputation and became an icon of Victorian culture, especially in the persona of "The Lady with the Lamp" making rounds of wounded soldiers at night. In 1860, Nightingale laid the foundation of professional nursing with the establishment of her nursing school at St Thomas' Hospital in London.
|
| 5 | 1822 | - 27 Dec 1822: Louis Pasteur born

Louis Pasteur (December 27, 1822 – September 28, 1895) was a French biologist, microbiologist and chemist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurization. His discoveries have saved many lives. He reduced mortality from puerperal fever, and created the first vaccines for rabies and anthrax. His medical discoveries provided direct support for the germ theory of disease and its application in clinical medicine. He is best known to the general public for his invention of the technique of treating milk and wine to stop bacterial contamination, a process now called pasteurization.
|
| 6 | 1824 | - 26 Jun 1824: Sir William Thomson Lord Kelvin born

William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 1824 – 17 December 1907) was a Scots-Irish mathematical physicist and engineer who was born in Belfast. At the University of Glasgow he did important work in the mathematical analysis of electricity and formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and did much to unify the emerging discipline of physics in its modern form. He also had a career as an electric telegraph engineer and inventor, which propelled him into the public eye and ensured his wealth, fame and honour. He had extensive maritime interests and was most noted for his work on the mariner's compass, which previously had limited reliability.
Absolute temperatures are stated in units of kelvin in his honour.
|


