| |
Date |
Event(s) |
| 1 | 1837 | - 20 Jun 1837—22 Jan 1901: Queen Victoria's reign

Victoria was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death. On 1 May 1876, she adopted the additional title of Empress of India.
Victoria inherited the throne at the age of 18, after her father's three elder brothers had all died leaving no surviving legitimate children. She became a national icon who was identified with strict standards of personal morality. Victoria married her first cousin Prince Albert. After his death in 1861, Victoria plunged into deep mourning and avoided public appearances. As a result, republicanism temporarily gained strength but in the latter half of her reign, her popularity recovered. Her Golden and Diamond Jubilees were times of public celebration.
|
| 2 | 1895 | - 25 Jun 1895—11 Jul 1902: Marquess of Salisbury - 49th British Prime Minister

Robert Arthur Talbot Gascoyne-Cecil, 3rd Marquess of Salisbury, (3 February 1830 – 22 August 1903), styled Lord Robert Cecil before 1865 and Viscount Cranborne from June 1865 until April 1868, was a British statesman and Conservative Party politician, serving as Prime Minister three times for a total of over thirteen years. He was the last Prime Minister to head his full administration from the House of Lords.
Among the important events of his premierships was the Scramble for Africa, culminating in the Fashoda Incident which escalated tensions with France, and the long, brutal and unpopular Second Boer War in South Africa.
|
| 3 | 1899 | - 4 Feb 1899—2 Jul 1902: Philippine–American War

The Philippine–American War, was an armed conflict between the First Philippine Republic and the United States that lasted from February 4, 1899, to July 2, 1902. While Filipino nationalists viewed the conflict as a continuation of the struggle for independence that began in 1896 with the Philippine Revolution, the U.S. government regarded it as an insurrection. The conflict arose when the First Philippine Republic objected to the terms of the Treaty of Paris under which the United States took possession of the Philippines from Spain, ending the short Spanish–American War.
The war, and especially the following occupation by the U.S., changed the culture of the islands, leading to the disestablishment of the Catholic Church in the Philippines as a state religion, and the introduction of English to the islands as the primary language of government, education, business, industry, and, in future decades, among upper-class families and educated individuals.
- 2 Oct 1899—7 Sep 1901: Boxer Rebellion

The Boxer Rebellion was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising that took place in China between 1899 and 1901, toward the end of the Qing dynasty. They were motivated by proto-nationalist sentiments and by opposition to Western colonialism and the Christian missionary activity that was associated with it.
The Boxer Protocol of 7 September 1901 provided for the execution of government officials who had supported the Boxers, provisions for foreign troops to be stationed in Beijing, and 450 million taels of silver—approximately $10 billion at 2018 silver prices and more than the government's annual tax revenue—to be paid as indemnity over the course of the next thirty-nine years to the eight nations involved. The Empress Dowager then sponsored a set of institutional and fiscal changes in a failed attempt to save the dynasty.
- 11 Oct 1899—31 May 1902: Second Boer War

Fought by Britain and her Empire against the descendants of the Dutch settlers (Boers) in the Transvaal region of South Africa, the Second Boer War highlighted the limitations of 19th C military methods, employing for the first time modern automatic weapons and high explosives to decimate the enemy
|
| 4 | 1901 | - 22 Jan 1901—6 May 1910: King Edward VII's reign

Edward VII was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The eldest son of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert, Edward was related to royalty throughout Europe. During his mother's long reign he was excluded from political power, and personified the fashionable, leisured elite. Despite public approval his reputation as a playboy prince soured his relationship with his mother.
As king, Edward fostered good relations between Britain and other European countries, especially France, for which he was popularly called "Peacemaker", but his relationship with his nephew, the German Emperor Wilhelm II, was poor. The Edwardian era, which covered Edward's reign and was named after him, coincided with the start of a new century and heralded significant changes in technology and society, including steam turbine propulsion and the rise of socialism
|
| 5 | 1902 | - 12 Jul 1902—4 Dec 1905: Arthur Balfour - 50th British Prime Minister

Arthur James Balfour, 1st Earl of Balfour, (25 July 1848 – 19 March 1930) was a British statesman and Conservative Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1905.
He oversaw reform of British defence policy and secured the Entente Cordiale with France, leaving Germany in the cold. Resignations from the Cabinet over tariffs left his party divided. He also suffered from public anger at the later stages of the Boer war and the importation of Chinese labour to South Africa.
- 8 Aug 1902: Paul Dirac born

Paul Dirac was an English theoretical physicist and one of the pioneers in quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics. He proposed the existence of anti-matter purely on the basis of his mathematical logic. The winner of several prestigious awards including the 1933 Nobel Prize for physics which he shared with Erwin Schrödinger, he turned down a knighthood as he did not want to be addressed by his first name.
|
| 6 | 1905 | - 5 Dec 1905—5 Apr 1908: Henry Campbell-Bannerman - 51st British Prime Minister

Sir Henry Campbell-Bannerman (7 September 1836 – 22 April 1908) was a British statesman and Liberal Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1905 to 1908. He was the first First Lord of the Treasury to be officially called "Prime Minister", the term only coming into official usage five days after he took office.
When Arthur Balfour resigned as Prime Minister, Edward VII invited Campbell-Bannerman to form a minority government as the first Liberal Prime Minister of the 20th century. At 69, he was the oldest person to become Prime Minister for the first time in the 20th century. He almost immediately dissolved Parliament and called a general election.
|
| 7 | 1907 | - 1 Jun 1907: Sir Frank Whittle born

Air Commodore Sir Frank Whittle, (1 June 1907 – 9 August 1996) was a British Royal Air Force air officer. He is credited with single-handedly inventing the turbojet engine. A patent was submitted by Maxime Guillaume in 1921 for a similar invention; however, this was technically unfeasible at the time. Whittle's jet engines were developed some years earlier than those of Germany's Hans von Ohain who was the designer of the first operational turbojet engine.
|
| 8 | 1908 | - 5 Apr 1908—5 Dec 1916: Herbert Henry Asquith - 52nd British Prime Minister

Herbert Henry Asquith, 1st Earl of Oxford and Asquith, (12 September 1852 – 15 February 1928), generally known as H. H. Asquith, was a British statesman and Liberal Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1908 to 1916.
He was the last prime minister to lead a majority Liberal government. He played a central role in the design and passage of major liberal legislation and a reduction of the power of the House of Lords. In August 1914, Asquith took Great Britain and the British Empire into the First World War. In 1915 his government was vigorously attacked for the shortage of munitions and the failure at Gallipoli. He formed a coalition government with the other parties but failed to satisfy critics. He was forced to resign in December 1916 and never regained power.
|
| 9 | 1910 | - 6 May 1910—20 Jan 1936: King George V's reign

George V's reign saw the rise of socialism, communism, fascism, Irish republicanism, and the Indian independence movement, all of which radically changed the political landscape. The Parliament Act 1911 established the supremacy of the elected British House of Commons over the unelected House of Lords. As a result of the First World War (1914–1918), the empires of his first cousins Tsar Nicholas II of Russia and Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany fell, while the British Empire expanded to its greatest effective extent.
In 1917, George became the first monarch of the House of Windsor, which he renamed from the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha as a result of anti-German public sentiment. In 1924 he appointed the first Labour ministry and in 1931 the Statute of Westminster recognised the dominions of the Empire as separate, independent states within the Commonwealth of Nations.
|
| 10 | 1912 | - 15 Apr 1912: Sinking of theTitanic

RMS Titanic sank in the early morning of 15 Apr 1912, 4 days into its maiden voyage from Southampton to New York. The largest liner in service at the time, her sinking killed over 1,500 people, one of the deadliest peacetime maritime disasters in history. The disaster caused widespread outrage over the lack of lifeboats, lax regulations, and unequal treatment of the 3 passenger classes during evacuation
- 23 Jun 1912: Alan Turing born

Computers owe their existence to British mathematician, Alan Turing. A child prodigy, he went on to pursue his PhD at Princeton University. He was an important member of a group of code-breakers in the Government Code and Cypher School in Bletchley Park and was given the daunting task of deciphering the ever-changing German codes sent by Enigma. He and his team of code-breakers were successful. Despite his part in ensuring the defeat of Germany he was prosecuted for his homosexuality, and committed suicide. In 2009 the British government issued a public apology for the way he was treated and in 2013 he was posthumously pardoned.
|
| 11 | 1914 | - 28 Jul 1914—11 Nov 1918: World War I

World War I (often abbreviated as WWI or WW1), also known as the First World War or the Great War, was a global war originating in Europe. Contemporaneously described as "the war to end all wars", it led to the mobilisation of more than 70 million military personnel, including 60 million Europeans, making it one of the largest wars in history. It was also one of the deadliest conflicts in history; an estimated nine million combatants and seven million civilians died as a direct result of the war, while resulting genocides and the 1918 influenza pandemic caused another 50 to 100 million deaths worldwide.
|
| 12 | 1915 | - 7 May 1915: Sinking of RMS Lusitania

The Sinking of RMS Lusitania occurred on Friday, 7 May 1915 during WWI, as Germany waged submarine warfare against the UK which had implemented a naval blockade of Germany. The ship was torpedoed by a U-boat and sank in 18 minutes, killing 1,198 and leaving 761 survivors. The sinking turned public opinion in many countries against Germany, and contributed to the American entry into WWI
|
| 13 | 1916 | - 1916: Maurice Wilkins born

Born in New Zealand, Maurice Wilkins was a biophysicist awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. He worked in the Manhattan project but lost interest in nuclear weapons and changed to biophysics. He and Rosalind Franklin provided the secondary research to the double helix theory. He shared the Nobel Prize with Watson and Crick as Franklin died in 1958.
- 24 Apr 1916—30 Apr 1916: Easter Rising

The Easter Rising was an armed insurrection in Ireland during Easter, launched by Irish republicans to end British rule in Ireland. 485 people were killed, over 2,600 wounded. Many of the civilians were killed as a result of the British using artillery and heavy machine guns, or mistaking civilians for rebels. Others were caught in the crossfire in a crowded city. It left parts of Dublin in ruins
- 8 Jun 1916: Francis Crick born

Francis Crick was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He is the co-discoverer of the structure of the DNA molecule. He, along with Watson and Maurice Wilkins were jointly awarded the 1962 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine ‘for their discoveries concerning the molecular structure of nucleic acids, the Double Helix and its significance for information transfer in living material’
- 6 Dec 1916—19 Oct 1922: David Lloyd George - 53rd British Prime Minister

David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor, (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was a British statesman and Liberal Party politician. He was the final Liberal to serve as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
As Chancellor of the Exchequer (1908–1915) during H. H. Asquith's tenure as Prime Minister, Lloyd George was a key figure in the introduction of many reforms which laid the foundations of the modern welfare state. His most important role came as the highly energetic Prime Minister of the Wartime Coalition Government (1916–22), during and immediately after the First World War. He was a major player at the Paris Peace Conference of 1919 that reordered Europe after the defeat of the Central Powers.
|
| 14 | 1917 | - 19 Jan 1917: Zimmermann Telegram
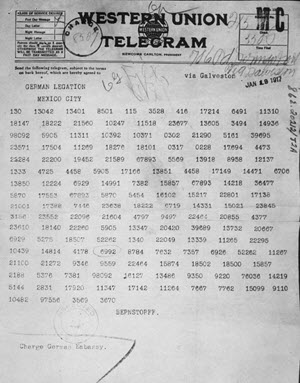
The Zimmermann Telegram (or Zimmermann Note or Zimmerman Cable) was a secret diplomatic communication issued from the German Foreign Office in January 1917 that proposed a military alliance between Germany and Mexico. In the event that the United States entered World War I against Germany, Mexico would recover Texas, Arizona and New Mexico. The telegram was intercepted and decoded by British intelligence. Revelation of the contents enraged Americans, especially after German Foreign Secretary Arthur Zimmermann publicly admitted the telegram was genuine on March 3, and helped generate support for the United States declaration of war on Germany in April. The decryption was described as the most significant intelligence triumph for Britain during World War I, and one of the earliest occasions on which a piece of signal intelligence influenced world events.
|
| 15 | 1918 | - 4 Mar 1918: 'Spanish' Flu
As WWI moved to its end the world was swept with a pandemic of epic proportions, killing more people than the fighting. It was called Spanish Flu because it only became widely reported when it reached neutral Spain, press censorship having suppressed news of it elsewhere. One theory is that it was brought to Europe by US Troops. patient zero having been traced to a military training camp in the United States
|
| 16 | 1920 | - 25 Jul 1920: Rosalind Franklin born

Rosalind Franklin was a renowned English chemist who did pioneering work in X-ray crystallography. Her most important discovery was the structure of DNA molecule. Working with Maurice Wilkins and a doctorate student Raymond Gosling, she was able to correctly assess the structure of DNA. Her theory that DNA consists of two helical structures was later confirmed by scientists James Watson and Francis Crick
|
| 17 | 1922 | - 23 Oct 1922—22 May 1923: Bonar Law - 54th British Prime Minister

Andrew Bonar Law (16 September 1858 – 30 October 1923), commonly called Bonar Law was a British Conservative politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1922 to 1923
Bonar Law was the shortest-serving PM of the 20th century. He is often referred to as "the unknown Prime Minister", not least because of a biography of that title by Robert Blake; the name comes from a remark by Asquith at Bonar Law's funeral, that they were burying the Unknown Prime Minister next to the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier. Sir Steven Runciman is reported to have said that he had known all British Prime Ministers in his lifetime, except Bonar Law whom no one knew.
|
| 18 | 1923 | - 22 May 1923—22 Jan 1924: Stanley Baldwin - 55th British Prime Minister

Stanley Baldwin, 1st Earl Baldwin of Bewdley, (3 August 1867 – 14 December 1947) was a British statesman and Conservative Party politician who dominated the government in his country between the world wars. Three times Prime Minister, he is the only British prime minister to have served under three monarchs.
Upon Bonar Law's resignation due to health reasons in May 1923, Baldwin became Prime Minister and Leader of the Conservative Party. He called an election on the issue of tariffs and lost the Conservatives' parliamentary majority, after which Ramsay MacDonald formed a minority Labour government.
|
| 19 | 1924 | - 22 Jan 1924—4 Nov 1924: Ramsay MacDonald - 56th British Prime Minister

James Ramsay MacDonald FRS (12 October 1866 – 9 November 1937) was a British statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1929 to 1935. He was the first Labour Party politician to become Prime Minister, leading minority Labour governments in 1924 and in 1929–31. He headed a National Government from 1931 to 1935, dominated by the Conservative Party and supported by only a few Labour members.
In 1924, his first priority was to undo the perceived damage caused by the 1919 Treaty of Versailles, by settling the reparations issue and coming to terms with Germany. The king noted in his diary, "He wishes to do the right thing.... Today 23 years ago dear Grandmama died. I wonder what she would have thought of a Labour Government!"
- 4 Nov 1924—4 Jun 1929: Stanley Baldwin - 57th British Prime Minister

Stanley Baldwin, 1st Earl Baldwin of Bewdley, (3 August 1867 – 14 December 1947) was a British statesman and Conservative Party politician who dominated the government in his country between the world wars. Three times Prime Minister, he is the only British prime minister to have served under three monarchs.
Baldwin's second government saw reforms in areas formerly associated with the Liberal Party. They included industrial conciliation, unemployment insurance, a more extensive old-age pension system, slum clearance, more private housing, and expansion of maternal and childcare. His government also saw the General Strike in 1926 and the Trade Disputes and Trade Unions Act 1927 to curb the powers of trade unions.
|
| 20 | 1926 | - 26 Jan 1926: First TV

John Logie Baird makes the first public demonstration of a mechanical television on 26 January at Selfridge's department store in London (the first successful transmissions were in early 1923 and February 1924). Later, in July 1928, he demonstrated the first colour television.
|
| 21 | 1928 | - 1928: Votes for Women

The Representation of the People (Equal Franchise) Act 1928 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. This act expanded on the Representation of the People Act 1918 which had given some women the vote in Parliamentary elections for the first time after World War I. The 1928 Act widened suffrage by giving women electoral equality with men. It gave the vote to all women over 21 years old, regardless of property ownership. Prior to this act only women over 30 who met minimum property qualifications could vote.
- 6 Apr 1928: James Watson born

James Watson is an American molecular biologist, geneticist and zoologist who co-discovered the molecular structure of DNA. His discovery has been described by other biologists and Nobel laureates as the most important scientific discovery of the 20th C. Crick, Wilkins and Watson discovered the double helix structure of the DNA molecule
- 28 Sep 1928: Discovery of Pennicillin

The effects of penicillium mould were isolated in 1928 by Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming, in his laboratory in the basement of St Mary's Hospital in London (now part of Imperial College). Fleming coined the term "penicillin"
|
| 22 | 1929 | - 1929: Martin Luther King born

MartinLuther King Jr was a leader of the African-American Civil Rights Movement. While fighting injustice meted out to African-Americans, he shunned violence. He used Christian doctrines but he looked towards Mahatma Gandhi’s non-violent movement. He dreamt that one day every human being would be judged by their ability, not skin colour. He died from a white fanatic’s bullet aged 39
- 5 Jun 1929—7 Jun 1935: Ramsay MacDonald - 58h British Prime Minister

James Ramsay MacDonald FRS (12 October 1866 – 9 November 1937) was a British statesman who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1929 to 1935. He was the first Labour Party politician to become Prime Minister, leading minority Labour governments in 1924 and in 1929–31. He headed a National Government from 1931 to 1935, dominated by the Conservative Party and supported by only a few Labour members.
MacDonald's second government was in a stronger parliamentary position than his first, and in 1930 he was able to raise unemployment pay, pass an act to improve wages and conditions in the coal industry (i.e. the issues behind the General Strike) and pass a housing act which focused on slum clearances. In 1931, in the aftermath of the Great Depression, he was forced to form a National Government with the Conservatives and Liberals.
- 4 Sep 1929: The Great Depression

The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression that took place mostly during the 1930s, beginning in the United States. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations; in most countries it started in 1929 and lasted until the late-1930s. It was the longest, deepest, and most widespread depression of the 20th century.
The Great Depression started in the United States after a major fall in stock prices that began around September 4, 1929, and became worldwide news with the stock market crash of October 29, 1929 (known as Black Tuesday). Between 1929 and 1932, worldwide gross domestic product (GDP) fell by an estimated 15%. By comparison, worldwide GDP fell by less than 1% from 2008 to 2009 during the Great Recession. Some economies started to recover by the mid-1930s. However, in many countries the negative effects of the Great Depression lasted until the beginning of World War II.
|
| 23 | 1932 | - 1932: Jet Engine Patented

RAF College Cranwell cadet Frank Whittle submitted his initial design for a turbo-jet to his superiors in 1928. It was whilst writing his thesis at the RAF College that Frank Whittle first developed the fundamental concepts of the turbojet engine. He was awarded his first patent for it in 1932. He spent a few more years actually building one, with the first running example being completed in 1937.
- Dec 1932: Enigma cracked

Cryptanalysis enabled the WWII Allies to read Enigma-enciphered Morse-coded communications of the Axis powers. The Enigma machines were portable cipher machines. Good operating procedures would have made them unbreakable but most of the German agencies that used Enigma used flawed procedures. It was broken by a Polish Cipher Bureau in Dec 1932, with the aid of French-supplied intelligence material obtained from a German.
|
| 24 | 1933 | - 1933: The London Underground Map
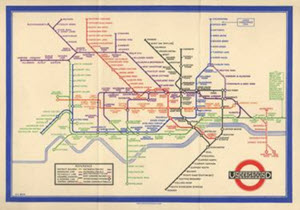
In 1933, Harry Beck's iconic, diagrammatic map of the London Underground appeared for the first time. Existing maps were not easy to follow because they reflected the topography above ground. Beck realised that, once underground, passengers need not be bound by what lay above, and he could lay out the map in a simpler way that was easier to understand, a system that has been copied on metro system across the world.
- 4 Mar 1933—12 Apr 1945: Franklin D. Roosevelt - 32nd US President

Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882 – April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American statesman and political leader who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945.
A Democrat, he won a record four presidential elections and became a central figure in world events during the first half of the 20th century. Roosevelt directed the federal government during most of the Great Depression, implementing his New Deal domestic agenda in response to the worst economic crisis in US history. As a dominant leader of his party, he built the New Deal Coalition, which realigned American politics into the Fifth Party System and defined American liberalism throughout the middle third of the 20th century. He is often rated by scholars as one of the three greatest U.S. presidents, along with George Washington and Abraham Lincoln.
|
| 25 | 1935 | - 7 Jun 1935—28 May 1937: Stanley Baldwin - 59th British Prime Minister

Stanley Baldwin, 1st Earl Baldwin of Bewdley, (3 August 1867 – 14 December 1947) was a British statesman and Conservative Party politician who dominated the government in his country between the world wars. Three times Prime Minister, he is the only British prime minister to have served under three monarchs.
With MacDonald's health in decline, he and Baldwin changed places: Baldwin was now Prime Minister, MacDonald Lord President of the Council. In October that year Baldwin called a general election. advised to make rearmament the leading issue in the election campaign against Labour, Baldwin said he would support the League of Nations, modernise Britain's defences and remedy deficiencies; but he also said: "I give you my word that there will be no great armaments". The main issues in the election were housing, unemployment and the special areas of economic depression
- 16 Nov 1935: Sir Magdi Yacoub born

Sir Magdi Yacoub is one of the world's most respected cardiac surgeons. Born in Egypt, he decided early on that he wanted to become a doctor and help others. He studied medicine at Cairo University and thereafter moved to the UK Most of his innovations and pioneering work in the field of heart surgery came during his stint in the hospitals in UK He is well known for his innovations in tissue engineering, myocardial regeneration, and transplant immunology.
|
| 26 | 1936 | - 20 Jan 1936—11 Dec 1936: King Edward VIII's reign

Edward VIII was king of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Empire, and emperor of India, from 20 January 1936 until his abdication on 11 December the same year, after which he became the Duke of Windsor.
Edward became king on his father's death in early 1936. Only months into his reign, he caused a constitutional crisis by proposing to Wallis Simpson, an American who had divorced her first husband and was seeking a divorce from her second. The prime ministers of the UK and the Dominions opposed the marriage, arguing a divorced woman with two living ex-husbands was politically and socially unacceptable as a prospective queen consort. When it became apparent he could not marry Wallis and remain on the throne, Edward abdicated. He was succeeded by his younger brother, George VI.
- 5 Oct 1936: Jarrow March

The Jarrow March was a protest against the unemployment and poverty suffered in the English Tyneside town of Jarrow during the 1930s. Around 200 men marched from Jarrow to London, carrying a petition to the British government requesting the re-establishment of industry in the town. They went home believing they had failed. In subsequent years, the Jarrow March became recognised as a defining event of the 1930s
- 12 Dec 1936—6 Feb 1952: King George VI's reign

George VI was king of the United Kingdom and the Dominions of the British Commonwealth from 11 December 1936 until his death in 1952. He was the last emperor of India and the first head of the Commonwealth.
As the second son of King George V, George VI was not expected to inherit the throne and spent his early life in the shadow of his elder brother, Edward who ascended the throne upon the death of their father in 1936. However, later that year Edward abdicated to marry divorcee Wallis Simpson, and George ascended the throne as the third monarch of the House of Windsor.
|
| 27 | 1937 | - 28 May 1937—10 May 1940: Neville Chamberlain - 60th British Prime Minister

Arthur Neville Chamberlain (18 March 1869 – 9 November 1940) was a British statesman and Conservative Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from May 1937 to May 1940.
Chamberlain is best known for his foreign policy of appeasement, and in particular for his signing of the Munich Agreement in 1938, conceding the German-speaking Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia to Germany. When Adolf Hitler invaded Poland, the UK declared war on Germany on 3 September 1939, and Chamberlain led Britain through the first eight months of the Second World War. Chamberlain resigned the premiership on 10 May 1940, as he believed that a government supported by all parties was essential, and the Labour and Liberal parties would not join a government headed by him.
|
| 28 | 1939 | - 3 Sep 1939—2 Sep 1945: World War II

World War II (often abbreviated to WWII or WW2.) The vast majority of the world's countries - including all the great powers - eventually formed two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. A state of total war emerged, directly involving more than 100 million people from over 30 countries. The major participants threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. WWII was the deadliest conflict in human history, marked by 50 to 85 million fatalities, most of whom were civilians in the Soviet Union and China. It included massacres, the genocide of the Holocaust, strategic bombing, premeditated death from starvation and disease, and the only use of nuclear weapons in war.
- 29 Sep 1939: 1939 Register

The National Registration Act 1939 established a National Register which began operating on 29 September 1939 (National Registration Day), a system of identity cards, and a requirement that they must be produced on demand or presented to a police station within 48 hours.
|
| 29 | 1940 | - 10 May 1940—26 Jul 1945: Winston Churchill - 61st British Prime Minister

Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill (30 November 1874 – 24 January 1965) was a British politician, statesman, army officer, and writer, who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1940 to 1945 and again from 1951 to 1955. As Prime Minister, Churchill led Britain to victory in the Second World War. Ideologically an economic liberal and British imperialist, he began and ended his parliamentary career as a member of the Conservative Party, which he led from 1940 to 1955, but for twenty years from 1904 he was a prominent member of the Liberal Party.
Widely considered one of the 20th century's most significant figures, Churchill remains popular in the UK and Western world, where he is seen as a victorious wartime leader who played an important role in defending liberal democracy from the spread of fascism. Also praised as a social reformer and writer, among his many awards was the Nobel Prize in Literature.
- 10 Jul 1940—31 Oct 1940: Battle of Britain

The Battle of Britain: RAF Fighter Command thwarted the Luftwaffe's attempts to gain air supremacy over southern England, averting invasion and downing 1,733 German aircraft. This came at a cost: 915 British aircraft were lost and about 544 of 2,927 RAF aircrew. Their numerical disadvantage prompted the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill to say 'Never in the field of human conflict was so much owed by so many to so few.'
|
| 30 | 1941 | - 22 Jun 1941: Operation Barbarossa begins

The German invasion of Russia – Operation Barbarossa begins. More than 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invade the USSR along a front stretching almost 3,000 km – the largest military operation in history would also result in the largest casualty rate
- 7 Dec 1941: Pearl Harbour Bombed

The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii Territory, on the morning of December 7, 1941.
The surprise attack came as a profound shock to the American people and led directly to the American entry into World War II in both the Pacific and European theatres. There were precedents for unannounced military action by Japan, but the lack of any formal warning, particularly while negotiations were still apparently ongoing, led President Franklin D. Roosevelt to proclaim December 7, 1941, "a date which will live in infamy". Because the attack happened without a declaration of war and without explicit warning, the attack on Pearl Harbor was later judged in the Tokyo Trials to be a war crime.
|
| 31 | 1942 | - 8 Jan 1942: Stephen Hawking born

Stephen William Hawking was an English theoretical physicist, cosmologist, and author, who was director of research at the Centre for Theoretical Cosmology at the University of Cambridge at the time of his death. He was the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge between 1979 and 2009.
Hawking achieved commercial success with works of popular science in which he discussed his own theories and cosmology in general. His book A Brief History of Time appeared on the British Sunday Times best-seller list for a record-breaking 237 weeks. He was a fellow of the Royal Society (FRS), a member of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences, and a recipient of the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the highest civilian award in the United States.
In 1963, Hawking was diagnosed with an early-onset slow-progressing form of motor neurone disease that gradually paralysed him. He died on 14 March 2018 at the age of 76, after more than 50 years battling the disease.
|
| 32 | 1943 | - 1943: First Computer
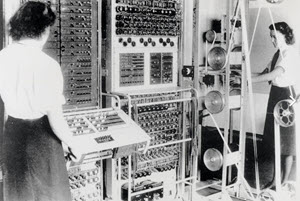
Colossus was a set of computers developed by British codebreakers in the years 1943–1945 to help in the cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher. Colossus used thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) to perform Boolean and counting operations. Colossus is thus regarded as the world's first programmable, electronic, digital computer, although it was programmed by switches and plugs and not by a stored program.
The existence of the Colossus machines was kept secret until the mid-1970s, although some of its personnel and secret information undoubtedly fueled further development in the U.S. in the late 1940s; the machines and the plans for building them were destroyed in the 1960s as part of the effort to maintain the secrecy of the project. This deprived most of those involved with Colossus of the credit for pioneering electronic digital computing during their lifetimes.
|
| 33 | 1944 | - 6 Jun 1944: D Day Landings

“We cannot afford to fail.” General Eisenhower, Supreme Commander. The British and American airborne armada began its mission. They landed at the edges of the invasion area on the Normandy coast to secure the western and eastern flanks of the beachheads to protect them from German attacks. Failure would see Hitler given the opportunity for an 11th-hour attempt to save Germany and launch his new V-weapons against British cities.
- 23 Jul 1944: First Liberation of Concentration Camp

Concentration Camps were erected in Germany from Mar 1933 after Hitler became Chancellor. Used to hold and torture political opponents and union organizers, the camps initially held around 45,000 prisoners and reached a monstrous 715,000 in January 1945
The first major camp, Majdanek, was discovered by the advancing Soviets on July 23, 1944.
|
| 34 | 1945 | - 12 Apr 1945—20 Jan 1953: Harry S. Truman - 33rd US President

Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884 – December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States (1945–1953), succeeding upon the death of Franklin D. Roosevelt after serving as vice president. He implemented the Marshall Plan to rebuild the economy of Western Europe, and established the Truman Doctrine and NATO.
Soon after succeeding to the presidency he became the only world leader to have used nuclear weapons in war. Truman's administration engaged in an internationalist foreign policy and renounced isolationism. He rallied his New Deal coalition during the 1948 presidential election and won a surprise victory that secured his own presidential term.
- 8 May 1945: VE Day

For days, people had been anticipating the German surrender – bell ringers were on-hand to ring in victory at St Paul’s Cathedral, while across the country Union Jack flags and bunting were ready for the celebrations that would come. On 8 May 1945 unconditional surrender was signed and the news the world had been waiting for arrived. War in Europe was over!
- 26 Jul 1945—26 Oct 1951: Clement Attlee - 62nd British Prime Minister

Clement Richard Attlee, 1st Earl Attlee, (3 January 1883 – 8 October 1967) was a British statesman and Labour Party politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1945 to 1951.
Following the end of the War in Europe, Attlee and Churchill favoured the coalition government remaining in place until Japan had been defeated. However, Herbert Morrison made it clear that the Labour Party would not be willing to accept this, and Churchill was forced to call an immediate election.
Labour won by a huge landslide, winning 393 seats in the House of Commons, a working majority of 146. This was the first time in history that the Labour Party had won a majority in Parliament.
- 15 Aug 1945: VJ DAY

While the war in Europe ended in May it continued in the Far East. The Japanese finally surrendered on 14 August following the dropping of the atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The next day, Wednesday 15 August 1945 was celebrated as VJ (Victory over Japan) Day. The official US commemoration is September 2. The name, V-J Day, had been selected by the Allies after they named V-E Day for the victory in Europe.
- 24 Oct 1945: United Nations Founded

The United Nations is an international organization founded in 1945 after the Second World War by 51 countries committed to maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations and promoting social progress, better living standards and human rights. The UN has 4 main purposes
1. To keep peace throughout the world
2. To develop friendly relations among nations
3. To help nations work together to improve the lives of poor people, to conquer hunger, disease and illiteracy, and to encourage respect for each other’s rights and freedoms
4. To be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations to achieve these goals
- 20 Nov 1945—1 Sep 1946: Nuremberg Trials begin

The Nuremberg trials were a series of military trials held by the Allied forces under international law and the laws of war after WWII to prosecute prominent members of the leadership of Nazi Germany who had any role in the Holocaust and other war crimes. The First trial was of the major war criminals before the International Military Tribunal - 24 of the most important political and military leaders of the Third Reich – Bormann was tried in absentia, while Robert Ley committed suicide within a week of the trial's commencement.
|